
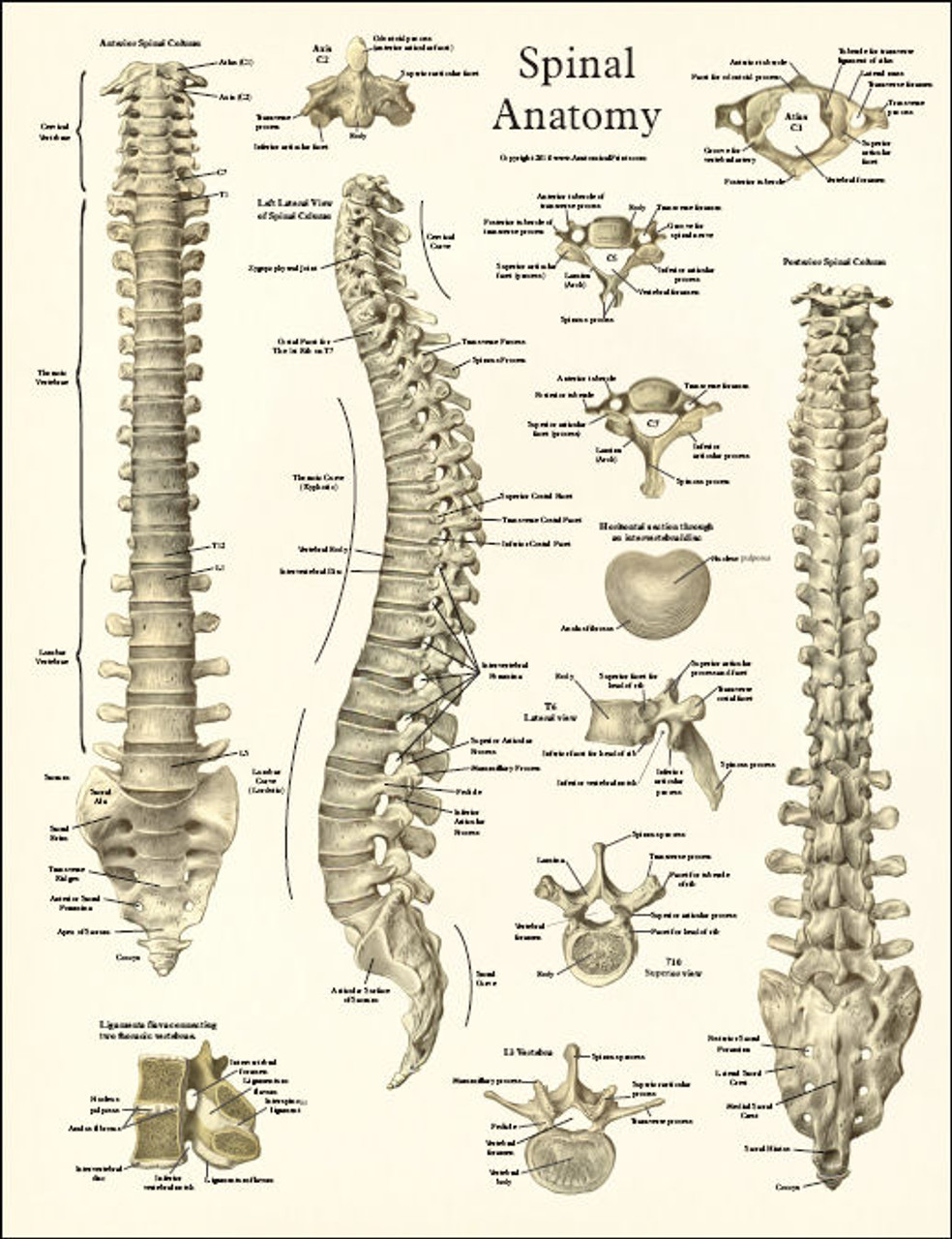
The lumbar vertebrae are the largest and carry most of the body’s weight. The Lumbar Spine consists of 5 vertebrae abbreviated L1-L5. The rib cage and ligaments limit range of motion and protect many vital organs. Rib attachments add to strength and stability the thoracic spine. The thoracic vertebrae are larger than the cervical bones and have longer spinous processes. T1 is the smallest and T12 is the largest thoracic. Thoracic Spineīeneath the last cervical vertebra are 12 Thoracic vertebrae abbreviated T1-T12 (top to bottom). The other cervical vertebrae (C3-C7) are shaped like boxes with small spinous processes (finger-like projections) that extend from the back of the vertebrae. Together, the Atlas and Axis enable the head to rotate and turn. It is circular in shape with a blunt tooth-like structure (called the Odontoid Process or dens) that projects upward into the Atlas. The Atlas is ring-shaped and supports the skull.
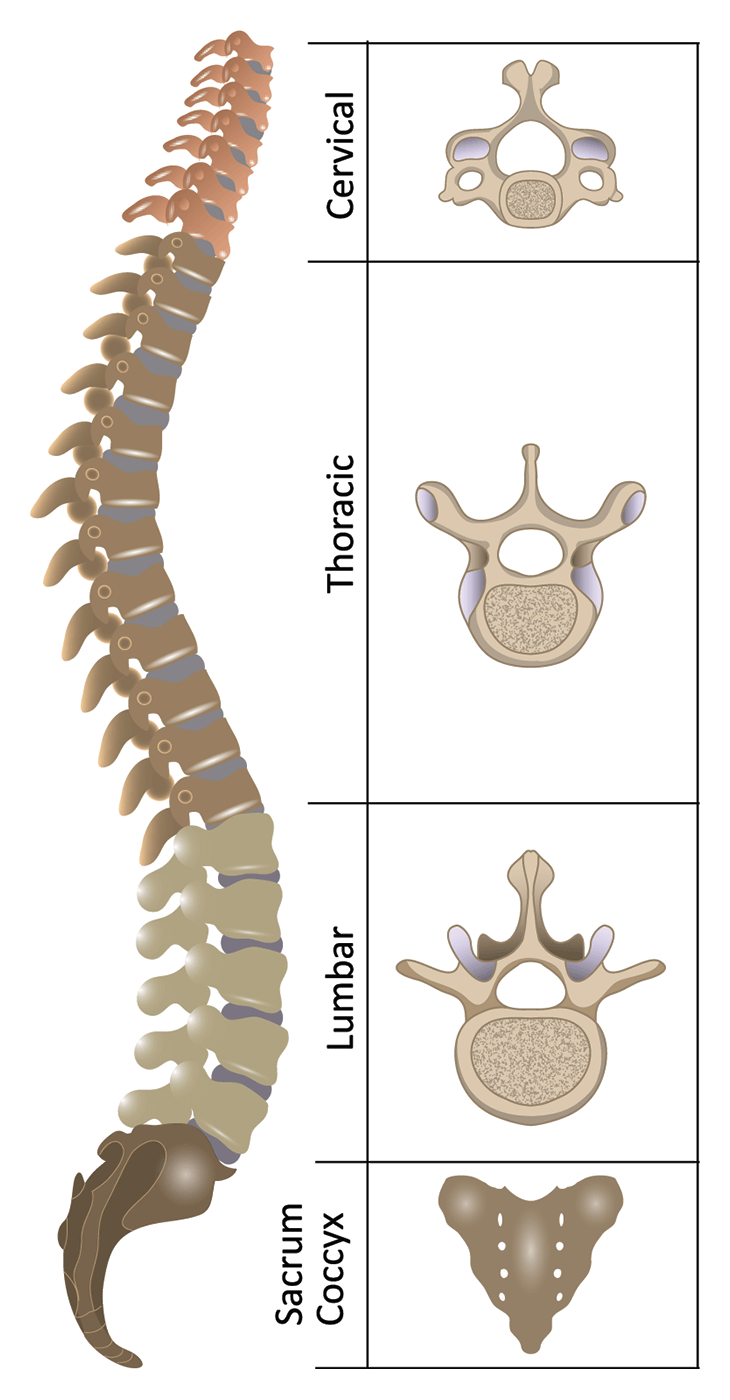
The first cervical vertebra (C1) is called the Atlas. These vertebrae protect the brain stem and the spinal cord, support the skull, and allow for a wide range of head movement. This region consists of seven vertebrae, which are abbreviated C1 through C7 (top to bottom). The regions of the spine consist of the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral. Provide structural support and balance to maintain an upright posture.Protect the spinal cord, nerve roots and several of the body’s internal organs.The three main functions of the spine are to: This information provides a straightforward overview of the spine’s remarkable and complex anatomy. Dorsal and ventral roots merge, exit the intervertebral foramina to become spinal nerves.Home > Education > Anatomy > Overview of the Spine Understanding Spinal Anatomy: Overview of the SpineĪ basic understanding of the spine’s anatomy and its functions is extremely important to patients with spinal disorders. Ventral roots contain axons from motor brain and spinal cord to the periphery. The ganglia contain the sensory neurons whose axons travel into the spinal cord via the dorsal roots. Each level of the spinal cord is associated with a pair of dorsal root ganglia, located outside the cord. These axons transmit information along the spinal cord. The white matter is located outside the grey matter and is made of myelinated motor and sensory axons. The grey matter also contains neurons projecting their axons to mediate autonomic control of the visceral organs. Motor neurons of the ventral horn project their axons to innervate skeletal and smooth muscles that control voluntary and involuntary reflexes. The lateral projections of the grey matter are called horns. The grey matter, with a butterfly shape located in the centre of the cord, contains the interneurons and motor neurons. This fluid is produced in brain cavities (the ventricles) to cushion both the brain and spinal cord. Similar to the brain, the spinal cord is enclosed by a membrane, the meninges, and is embedded in a liquid, the cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal canal plays the important role to direct and protect the spinal cord. It has a length of 40-50 cm and a diameter of approximately 1-1.5 cm. It runs from the skull, through the spinal canal up to the first lumbar vertebra. The spinal cord is a bundle of nerves originating from the brain reaching out to the limbs and internal organs. Many nerve endings supply the annulus and, as a result, an injury to the annulus causes pain and neurological symptoms. The annulus maintains the strength of the spine and acts as shock absorber. In standing position the weight draws onto the nucleus allowing it to expand whilst the ring will keep it in place. It consists of several layers, similar to elastic bands, which adapt to vertebral movements. Nucleus pulposus located at the centre filled with a jelly-like material providing flexibility and strength.Īnnulus Fibrosus is the flexible outer ring of the disc. They are flat and round, with a thickness of about a half-inch and are made up of two parts: Because of their position, the intervertebral discs prevent friction between the vertebrae. They are very important structures for the The intervertebral discs are positioned between the vertebrae to absorb the stress of the spine and facilitate the movement. The rim of the body is thicker to provide a concave form. The anatomy of the vertebrae includes a body with a large oval shape made by the strongest bone structure. The cavity in the centre, or foramen, is only present in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae and is occupied by the spinal cord and its nerves. They are round-shaped bones piled up to form the spinal column. The vertebrae are the main constituents of the spine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
